
Getty Photographs
Researchers on Wednesday reported essential vulnerabilities in a broadly used networking equipment that leaves a few of the world’s largest networks open to intrusion.
The vulnerabilities reside in BIG-IP Subsequent Central Supervisor, a element within the newest technology of the BIG-IP line of home equipment, which organizations use to handle visitors going into and out of their networks. Seattle-based F5, which sells the product, says its gear is utilized in 48 of the highest 50 companies as tracked by Fortune. F5 describes the Subsequent Central Supervisor as a “single, centralized level of management” for managing total fleets of BIG-IP home equipment.
As gadgets performing load balancing, DDoS mitigation, and inspection and encryption of information getting into and exiting massive networks, BIG-IP gear sits at their perimeter and acts as a significant pipeline to a few of the most security-critical assets housed inside. These traits have made BIG-IP home equipment ideally suited for hacking. In 2021 and 2022, hackers actively compromised BIG-IP home equipment by exploiting vulnerabilities carrying severity rankings of 9.8 out of 10.
On Wednesday, researchers from safety agency Eclypsium reported discovering what they mentioned have been 5 vulnerabilities within the newest model of BIG-IP. F5 has confirmed two of the vulnerabilities and launched safety updates that patch them. Eclypsium mentioned three remaining vulnerabilities have gone unacknowledged and it’s unclear if their fixes are included within the newest launch. Whereas the exploited vulnerabilities from 2021 and 2022 affected older BIG-IP variations, the brand new ones reside within the newest model, often called BIG-IP Subsequent. The severity of each vulnerabilities is rated as 7.5.
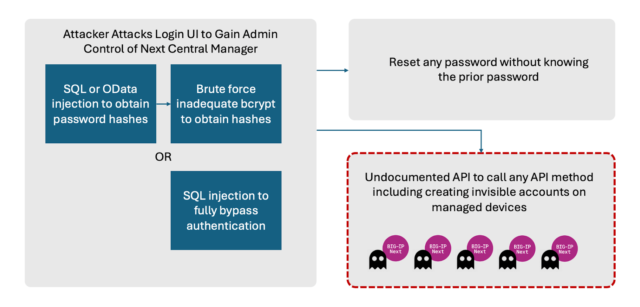
“BIG-IP Subsequent marks a very new incarnation of the BIG-IP product line touting improved safety, administration, and efficiency,” Eclypsium researchers wrote. “And because of this these new vulnerabilities are significantly important—they not solely have an effect on the latest flagship of F5 code, additionally they have an effect on the Central Supervisor on the coronary heart of the system.”
The vulnerabilities enable attackers to realize full administrative management of a tool after which create accounts on programs managed by the Central Supervisor. “These attacker-controlled accounts wouldn’t be seen from the Subsequent Central Supervisor itself, enabling ongoing malicious persistence throughout the atmosphere,” Eclypsium mentioned. The researchers mentioned they haven’t any indication any of the vulnerabilities are below lively exploitation.
Each of the mounted vulnerabilities might be exploited to extract password hashes or different delicate information that enable for the compromise of administrative accounts on BIG-IP programs. F5 described certainly one of them—tracked as CVE-2024-21793—as an Odata injection flaw, a category of vulnerability that permits attackers to inject malicious information into Odata queries. The opposite vulnerability, CVE-2024-26026, is an SQL injection flaw that may execute malicious SQL statements.
Eclypsium mentioned it reported three further vulnerabilities. One is an undocumented programming interface that permits for server-side request forgeries, a category of assault that beneficial properties entry to delicate inside assets which might be imagined to be off-limits to outsiders. One other is the power for unauthenticated directors to reset their password even with out understanding what it’s. Attackers who gained management of an administrative account may exploit this final flaw to lock out all professional entry to a susceptible system.
The third is a configuration within the bcrypt password hashing algorithm that makes it potential to carry out brute-force assaults towards thousands and thousands of passwords per second. The Open Internet Software Safety Challenge says that the bcrypt “work issue”—which means the quantity of assets required to transform plaintext into cryptographic hashes—needs to be set to a degree no decrease than 10. When Eclypsium carried out its evaluation, the Central Supervisor set it at six.
Eclypsium researchers wrote:
The vulnerabilities now we have discovered would enable an adversary to harness the ability of Subsequent Central Supervisor for malicious functions. First, the administration console of the Central Supervisor might be remotely exploited by any attacker in a position to entry the executive UI by way of CVE 2024-21793 or CVE 2024-26026. This could lead to full administrative management of the supervisor itself. Attackers can then make the most of the opposite vulnerabilities to create new accounts on any BIG-IP Subsequent asset managed by the Central Supervisor. Notably, these new malicious accounts wouldn’t be seen from the Central Supervisor itself.
All 5 vulnerabilities have been disclosed to F5 in a single batch, however F5 solely formally assigned CVEs to the two unauthenticated vulnerabilities. We have now not confirmed if the opposite 3 have been mounted on the time of publication.
F5 representatives didn’t instantly have a response to the report. Eclypsium went on to say:
These weaknesses can be utilized in quite a lot of potential assault paths. At a excessive degree attackers can remotely exploit the UI to realize administrative management of the Central Supervisor. Change passwords for accounts on the Central Supervisor. However most significantly, attackers may create hidden accounts on any downstream system managed by the Central Supervisor.
Eclypsium
The vulnerabilities are current in BIG-IP Subsequent Central Supervisor variations 20.0.1 by means of 20.1.0. Model 20.2.0, launched Wednesday, fixes the 2 acknowledged vulnerabilities. As famous earlier, it’s unknown if model 20.2.0 fixes the opposite habits Eclypsium described.
“If they’re mounted, it’s +- okay-ish, contemplating the model with them will nonetheless be thought of susceptible to different issues and want a repair,” Eclypsium researcher Vlad Babkin wrote in an e mail. “If not, the system has a long-term approach for an authenticated attacker to maintain their entry perpetually, which will likely be problematic.”
A question utilizing the Shodan search engine reveals solely three cases of susceptible programs being uncovered to the Web.
Given the current rash of lively exploits focusing on VPNs, firewalls, load balancers, and different gadgets positioned on the community edge, BIG-IP Central Supervisor customers would do effectively to put a excessive precedence on patching the vulnerabilities. The provision of proof-of-concept exploitation code within the Eclypsium disclosure additional will increase the probability of lively assaults.






